To finalise the series of articles about problem solving, we will look at Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
What is FMEA?
FMEA is a methodology developed towards the end of the 1940’s, by reliability engineers in the American Military. Recognised as one of the oldest structured reliability improvement methods, it is still as effective in today’s project environment.
Its aim is to foresee potential failure at the design stage by identifying issues in the design or manufacturing process. This allows manufacturers to reduce the risk of failure by taking action at an early stage.
The failure mode aspect of the process is ways in which it can fail, whereas effects describe how those failures can lead to undesirable outcomes, including defects and excess waste.
FMEA Categories
There are three main categories of FMEA, concept (CFMEA), design (DFMEA) and process (PFMEA).
Concept FMEA
CFMEA analyses concepts in the initial stages, prior to the definition of hardware, by focusing on potential failure modes connected with the proposed functions of a concept proposal. The interaction of assorted systems and multiple elements of a system are included in CFMEA.
Design FMEA
DFMEA is usually conducted at three levels, system, subsystem and component. It analyses products prior to production by focusing on the potential failure modes caused by design deficiencies. Hardware, functions or a combination of the two are the focus on DFMEA.
Process FMEA
PFMEA also works at system, subsystem and component levels, and analyses manufacturing and assembly processes, identifying process deficiencies that can lead to potential failure modes. PFMEA is closely aligned with customer care in many industries.
How is FMEA measured?
There are three criteria used to assess problems:
- How severely the problem has affected the customer.
- How frequently the problem is expected to occur.
- The ease of detecting the problem.
Each criteria is ranked between 1 and 10 (with 1 being the lowest). Once this has been decided amongst the team, each failure mode can be assigned a risk priority number (RPN) as follows:
RPN = severity x occurrence x detection
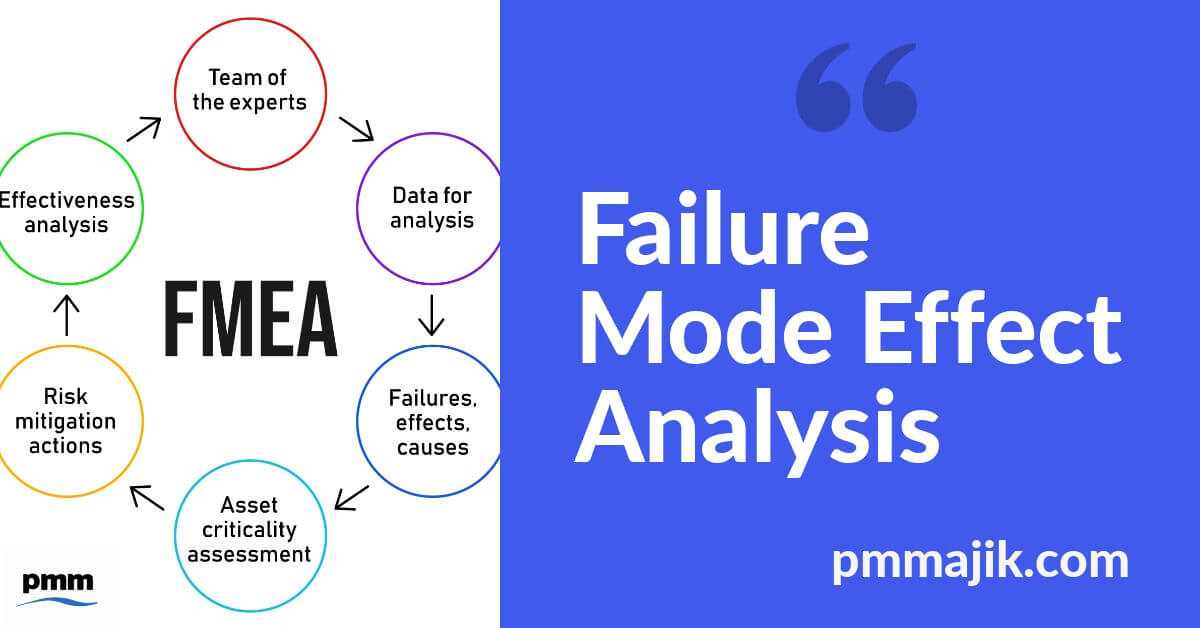
The FMEA process
The FMEA should be done in a step-by-step method, since each step builds upon the previous one. There are ten steps to follow.
Process review
The process flowchart should be used to identify each component; the components should then be listed in the FMEA table.
Depending on the size of the process, it may be necessary to break up the analysis into smaller sections.
Identify potential failures
The project team undertake brainstorming to identify potential failure modes, carefully reviewing data and documentation for signs. The list will be comprehensive with numerous potential failures listed for each component.
Once the initial list has been compiled, it can be reduced by combining similar items.
List possible effects of failures
How the potential failure will affect the end user, or the rest of the process, should be listed. As with the potential failures in the previous step, there may be multiple effects for each failure.
Rank the severity
Rank the failures from one to ten based on the severity of the consequences of failure.
Rank the occurrence
Rank the failures from one to ten based on how frequently it is likely it is to occur.
Rank the detection
Rank the failures based on the chances that it will be detected before it occurs.
Calculate the RPN
Use severity x occurrence x detection to calculate the RPN for each failure.
Construct an action plan
Identify which failures are to be worked on. The highest RPN’s should provide the starting point for the action plan.
Assign project members to failures and agree appropriate deadlines.
Action the plan
Implement the improvements that have been identified in the action plan.
Re-calculate the RPN
Once the improvements have been made, re-calculate the RPN to identify how effective the improvements have been.
A common problem-solving tool, Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) is effective in solving simple and more complex problems by identifying issues before they happen. Identifying failure modes early in the process can save an organisation a significant amount of money and delays to processing schedules.
Additional Resources
Take time to check the other articles on problem solving.