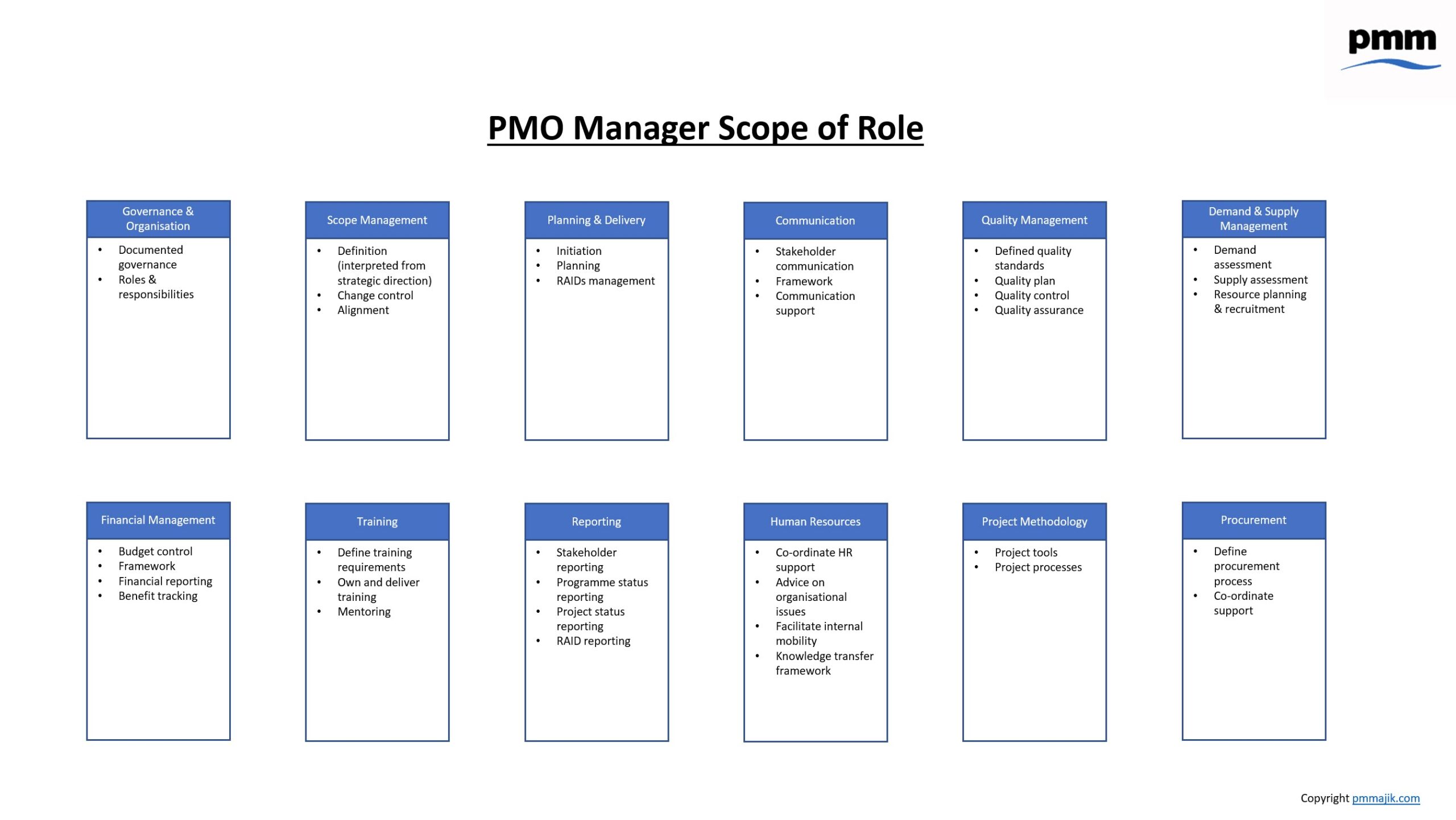
There is no such thing as a typical PMO. The very fact that all organisations are different in style, culture, principles, etc, means that an administrative PMO in one organisation will look different and behave differently than one in another organisation. The good news is that there is no right or wrong answer on how a PMO should look and behave, as long as it is “fit for purpose”.
However, while they may look and act differently, there should be a core set of functions that will (probably) be performed by a typical PMO.
PMO Functions
The diagram below gives an overview of the typical PMO functions and activities.
Governance
This provides the definition of how the projects, workstreams and PMO will be governed. It should capture the appropriate forum’s, meetings, steering committees, etc together with escalation paths and approval thresholds. This is particularly important for Change Requests and Business Case approvals.
Organisation
Documentation of PMO organisation to clearly identify roles. This should be accompanied with clear responsibilities.
Planning
Project planning is all of the activities to define scope, estimate costs and create a project schedule that will enable the desired outcome to be delivered.
Financial Management
Chapter 7 of the PMBOK is dedicated to project cost management and uses the following definition.
“Project Cost Management includes the processes involved in estimating, budgeting and controlling costs so that the project can be completed in the approved budget.”
PMO Cost Management provides a framework to complete the cost management activities in a standardised manner.
Benefits
Benefit Management is:
“The processes involved in estimating and monitoring benefits so that the value can be realised”.
PMO Benefit Realisation is the process of releasing the value of the benefits.
Benefits fall into 2 broad categories:
Tangible Benefit
This is typically a benefit that can be measured numerically i.e. reduction in costs, increase in profit, reduction in headcount, etc.
Tangible benefits tend to be easier to quantify and demonstrate that they have been achieved.
Intangible Benefit
These are more difficult to measure numerically i.e. reduction in operational risk, improve reputation, provide better customer experience, cost avoidance, etc.
RAIDs
The process of identifying, managing and reporting the risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies that may impact the successful delivery of a project. It allows informed decision making on what mitigation actions to take.
Reporting
The process of providing an accurate and timely update of the status of a project, programme or workstream so that there is common understanding of status. This allows the rapid identification of risks threatening the successful delivery of the project so that timely interventions can be made.
Quality Assurance
The process of reviewing the quality of project execution NOT the quality of the deliverables from each project i.e. delivery of software component. Ensuring the quality and discipline of project execution should result in a better quality of project delivery.
Change Control
Change Control is the formal process to ensure that changes to the agreed scope, schedule, benefits and budget of a project are introduced in a controlled and coordinated manner.
Resource Management
The process of identifying and adding the required resources to the project to enable successful delivery.
Communication Management
The PMBOK defines communication management as:
“The processes required to ensure timely and appropriate generation, collection, distribution, storage, retrieval and ultimate disposition of project information”.
Procurement Management
The PMBOK defines the procurement process as being:
“Project Procurement Management includes the processes necessary to purchase or acquire products, services or results needed from outside the project team. The organisation can be either the buyer or seller of the products, services or results of a project”.
In simple terms it is the process of getting the “stuff” needed to successfully deliver the project.
Document Storage
Project document storage is the standard approach to the naming and storage of all project documentation so that they are securely stored and can be easily accessed by all project and PMO members.
This is a very quick and high level overview of the typical PMO functions and activities. This will vary between different types of PMO. You can visit blog post How to set up a PMO for more information on each of these function.